We are regularly on the web researching useful sites, current news, and stories about victims and survivors of Elder Abuse. What follows are online resources that may be of use to the elderly and their adult children or other caregivers. The list is both long and likely incomplete. We welcome suggestions, additions and even subtractions. When we find a great site we will share it here. Do you have a site or story you would like to share? Please contact staff@kasemcares.com
WEB LINKS
- AARP
- Alzheimer’s Association
- Caregiver Resource Center
- Council on Aging
- The Ombudsman The Office of the Ombudsman examines complaints from members of the public who feel they have been unfairly treated by certain public bodies.
- Legal Aid Society
- Medicare
- Visitation Guide for California Long Term Care Facilities and Hospitals
- Silver Angels For the Elderly (S.A.F.E.): Our elderly need a voice. There are abuses that go on daily at our assisted livings, nursing homes or by private caregivers. We want to give our elderly, their loved ones, and caregivers a forum to have their complaints and fears about these abuses exposed on our website so that others can be aware of how to address these issues. “We will offer help, suggestions and whatever tools God has provided for us to help address these abuses and make people aware that they are not alone.”
- CANHR California Advocates for Nursing Home Reform (CANHR), a statewide nonprofit 501(c)(3) advocacy organization, has been dedicated to improving the choices, care and quality of life for California’s long term care consumers.
If You Need Immediate Help, Call:
Emergency: 911
Adult Protective Services (elder abuse) (800) 451-5155. If you need legal assistance: click here for recommendations based on your city, state.
HOUSING AND SERVICES
- National Center for Assisted Living. Provides a more elaborate “facility finder” that factors in cost, method of payment, mobility, dietary needs, activities and amenities.
- Living Your Choice. Living Your Choice helps you find the best senior living options by using a personalized hands on approach. This service is free.
- Visiting Nurse Associations of America. Search for home health services nationwide. Includes suggested questions to ask service providers.
- National Association of Professional Geriatric Care Managers. Search for a geriatric care manager by location.
- Homemods.org. Advice on home renovation from the University of Southern California.
- HealthGrades. Comparisons and one-to-five-star ranking of nursing homes, for $9.95 for the first report and $2.95 for each additional one.
- UCompareHealthCare. Free search by location for nursing homes, plus data on quality, staffing and outcomes from government sources. (Disclosure: Owned by The New York Times Co.)
- TheSeniorGuide.com. Search by state and region for all types of senior housing, case managers, lawyers and more. Includes a glossary of industry jargon.
- National Association of Senior Move Managers (NASMM). A not-for-profit, professional association dedicated to assisting older adults with the physical and emotional demands of downsizing, relocating, or modifying their homes.
- A Place for Mom
CAREGIVING & HEALTH
- National Alliance for Caregiving. Reviews of more than 1,000 books, videos, Web sites and links.
- Alzheimer’s Abuse. Alzheimer’s abuse cases are believed to occur in high rates because patients are often unable to communicate their experiences of elder mistreatment or abuse. As a result, many Alzheimer’s abuse cases go unnoticed or unreported. It is important for family members to visit a loved one if he or she is living in a nursing home or assisted living facility. By regularly visiting with elderly loved ones, the family is able to monitor any changes in mood, behavior, appearance, or health that may indicate Alzheimer’s abuse or neglect.
- National Family Caregivers Association. Provides statistics, research and policy reports, tip sheets, first-person accounts, a newsletter and an exhaustive resource list.
- MetLife Mature Market Institute. Reports from a research arm of the insurance company on the price of assisted living, the strains of long-distance caregiving, and the cost to employers of baby boomer employees involved in eldercare.
- Strength for Caring. A site for family caregivers from Johnson and Johnson with original articles written by experts and how-to materials.
- The Alzheimer’s Association.
LEGAL AND FINANCIAL
- BenefitsCheckUp. A search tool developed by the National Council on Aging to determine eligibility for 1,300 benefit programs that help pay for medications, health care, utilities and so forth.
- National Academy of Elder Law Attorneys. Search by location for members of the association. Provides questions to ask lawyers about qualifications and areas of expertise, and a wide-ranging resource list for the elderly.
- Nolo. Do-it-yourself legal advice. Wills, powers of attorney and other documents.
- U.S. Living Will Registry. Free state-by-state forms.
- American Bar Association Aging Tool Kit. Offers a 10-step process for making end-of-life decisions with worksheets, suggestions and links.
END OF LIFE
- The National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization. An excellent search tool for finding a hospice, as well as guides on issues related to palliative care, including Medicare coverage and techniques for communicating end-of-life wishes.
- Caring Connections. Contains of the consumer information from NHPCO and has state-by-state advance directive forms.
- Compassion and Choices.
- Hospice Foundation of America. Information on end-of-life issues, such as pain management. One section called “Caregivers Corner” has links, reading lists and a self-assessment tool for caregivers to analyze their own strengths and weaknesses.
AGING
- Medicare.gov. An all-purpose site with interactive tools for planning and paying for long-term care and choosing among drug plans. Includes searchable inspection results, good and bad, for the all the nation’s skilled nursing facilities.
- NIHSeniorHealth.gov. A collaboration of the National Institutes of Health and the National Library of Medicine that provides authoritative information on all diseases and disorders of old age. Each section is available in both large-type and audio versions.
- National Institute on Aging. Describes ongoing research on aging and lists clinical trials seeking participants.
- U.S. Administration on Aging. Brief fact sheets on aging and links to outside resources for an assortment of caregiving issues, including financial planning, residential options, in-home services, case management and the law.
MAGAZINES
WHAT IS ELDER ABUSE?
Elder abuse and/or neglect is an intentional action that results in harm or creates a significant risk of harm (whether or not harm is intended) to an elder (defined as age 60 or older) by a caregiver or any other person the elder trusts. This includes a failure to protect the elderly individual from harm and/or meet his or her basic needs.
The six most commonly identified types of elder abuse include:
1. Physical: This involves burning, hitting, slapping, pushing, kicking, or any other show of force.
2. Emotional: This involves behaviors that damage an elder’s self-worth or emotional well-being and includes destroying property, isolating the elder from friends and family, name calling, or deliberately scaring or embarrassing an elder.
3. Financial and/or material exploitation: This refers to the illegal misuse of an elder’s assets, money, or property.
4. Abandonment: This involves a caregiver leaving an elder alone and no longer providing care for him or her.
5. Neglect: This refers to the failure to meet an elder’s basic needs, such as clothing, medical care, housing, and food.
6. Sexual: This involves forcing an elder to participate in a sexual act in which the elder does not or cannot consent.
CLICK TO VIEW MORE INFORMATION
List your resource for our page. Contact us today!

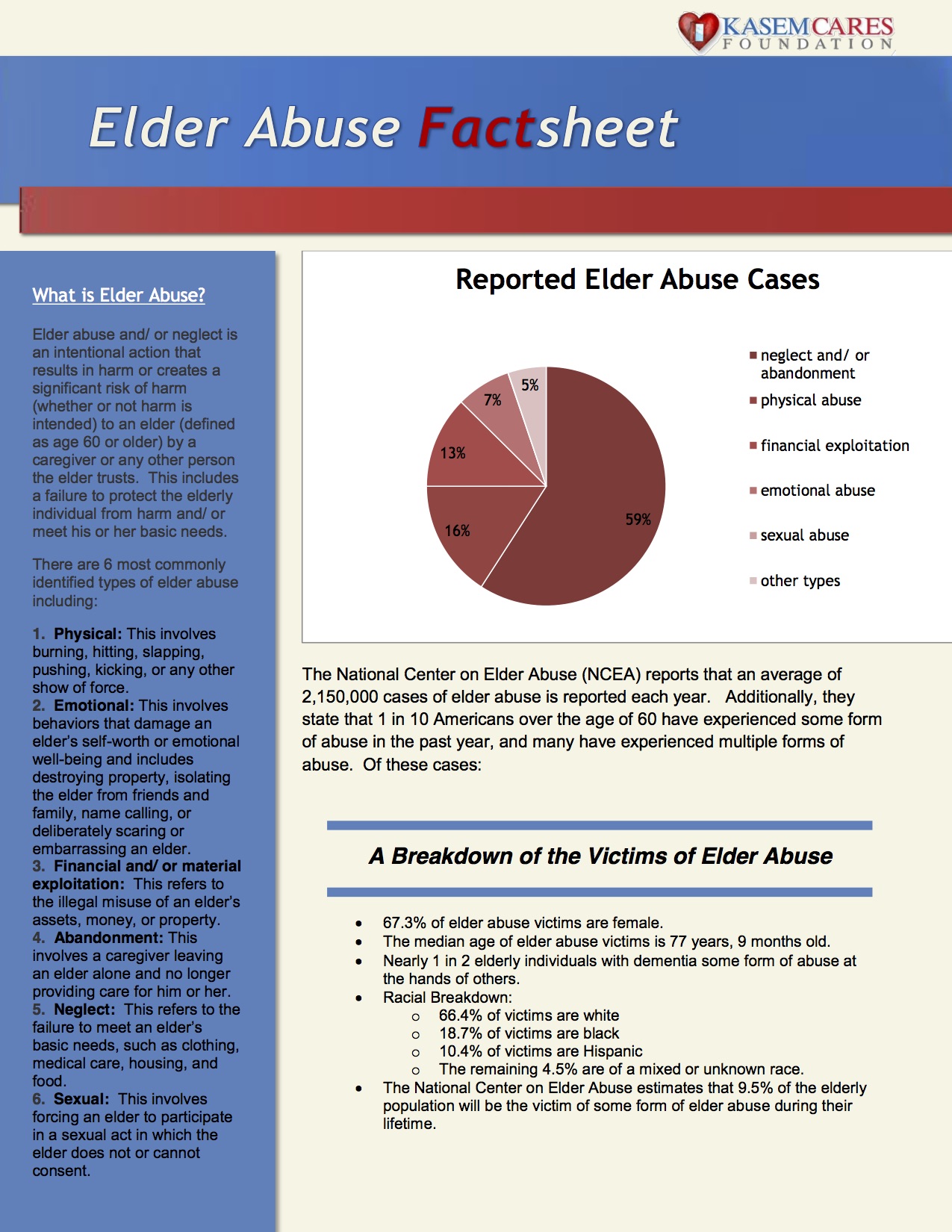

Elder Abuse Information – Stats & Facts: CLICK TO VIEW